Recent advances in technology have made it possible for diamonds to be created in labs. Lab-created diamonds have the same chemical composition and physical properties as earth-mined diamonds, making the two types of gemstone virtually indistinguishable from each other.
Unlike cheaper diamond variants, such as moissanite and cubic zirconia, lab diamonds exhibit the same scintillation, fire, and brilliance as mined diamonds and will not fade or discolour over time. This article will look in more detail at the origins of these man-made stones as well as their benefits.
How Are Lab Diamonds Made?
There are two main methods by which high-quality diamonds, identical to those sourced from the earth are made. These are: HPHT (high pressure high temperature) and CVD (chemical vapor deposition).
- The HPHT Method: This method of producing diamonds was first introduced in the 1950s. By subjecting carbon atoms to extremely high heat and pressure, this process seeks to replicate the conditions within the earth which causes the formation of diamonds, albeit at a much faster rate. This process is also used on natural or colourless diamonds to enhance their colour to produce other desirable stones which are pink, yellow, green or blue.A HPHT diamond is created by placing a small diamond seed into pure carbon. This is then exposed to extreme pressure and heat, similar to the natural conditions involved in the formation of diamonds beneath the earth’s crust. Temperatures typically range from 2,500 to 3,500 degrees Fahrenheit with pressure of about 70,000 atmospheres, which is approximately 70,000 times the pressure at sea level. As the carbon melts, a synthetic diamond begins to form around the seed. This lab-grown stone is then cooled to produce a diamond which can then be cut and polished.
- The CVD Method: This method of producing diamonds involves the chemical reaction of a hydrocarbon gas mixture and hydrogen to recreate the formation of diamonds within interstellar clouds of gas. The CVD method uses lower pressures and temperatures in a vacuum chamber compared to the HPHT method. A diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber which is then filled with gases and heated to around 1,500 to 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit.At these temperatures, the gas becomes plasma, releasing pieces of carbon that attach themselves to the diamond seed. The formation of the diamond, or crystallization, takes place over several weeks. These lab-grown diamonds are created for many purposes and provide benefits to different sectors, one of which is the diamond jewelry
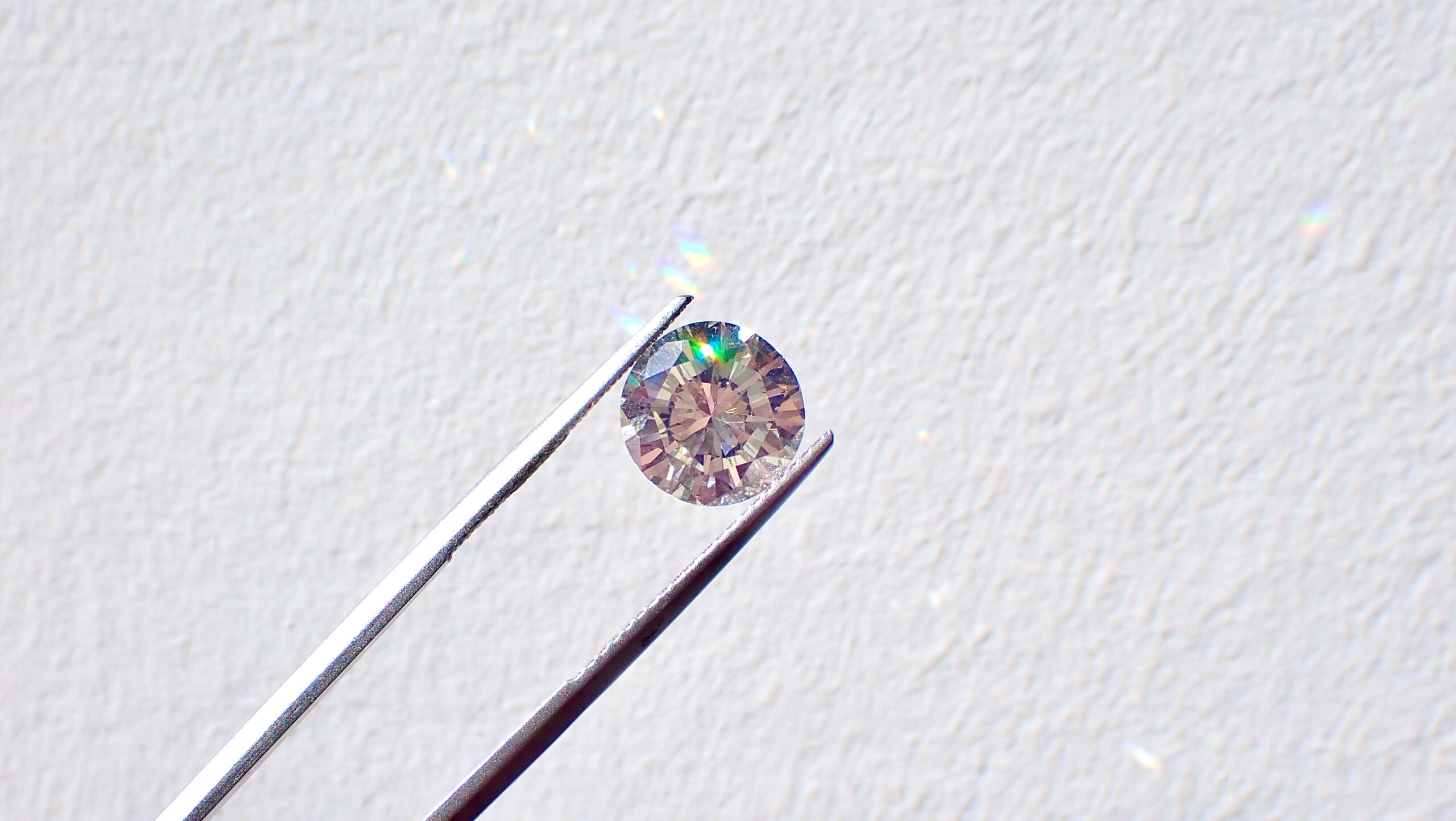
Lab-Created Diamond Rings
As the technology for producing lab-created diamond rings continues to improve and more entrants populate the industry, such diamond variants are becoming a popular choice for many consumers. The lab-grown diamond market share is estimated to grow to 10% of the global diamond market by 2030 with a market value expected to reach $29.2 billion by 2025. When it comes to selecting a stone for your partner, lab created diamond engagement rings have many benefits over traditional diamonds.
The extraction of diamonds from the earth can have devastating effects on the natural environment, contributing to soil erosion, deforestation and the destruction of ecosystems. Diamond mining has also been associated with many unethical practices including child labor and the financing of terrorism an insurgencies in war torn areas, coining the term ‘blood diamonds.’ As a result, for many people these diamonds have lost their sparkle. As well as being ethically courses some of the other benefits of lab-created diamond rings include the following:
- Affordability: Lab-grown diamonds can produce the same color, clarity and cut as naturally-sourced diamonds, however, as the process is far less labor-intensive it is a more cost-effective way to produce and, therefore, purchase a diamond. Prices of lab-grown diamonds are typically 40 to 60% cheaper than natural diamonds.
- Sustainability: Extracting diamonds from the Earth is unsustainable and continues to deplete a natural resource. Lab-created diamonds offer a more affordable and sustainable alternative.
- Variety: Lab-grown diamonds can be made in a variety of different colors and are available at a fraction of the price of their more rarer and more expensive natural counterparts.
- Quality: As they are produced in controlled lab conditions, these diamonds can produce clearer and brighter diamonds that have less imperfections or impurities than natural diamonds. This is why lab-grown diamonds often receive higher quality gradings compared to naturally-sourced diamonds.
Other applications for lab-created diamonds include for technological purposes such as surgical knives, laser lenses, cutting tools, quantum computing, semiconductors, anvils and more.
As this article has shown, there are many benefits and applications for lab-brown diamonds, making them a viable and strong competitor to traditional diamonds.

